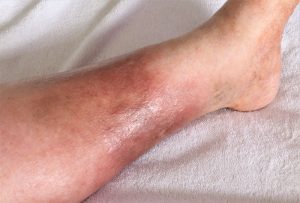
Edema occurs when there is accumulation of excess fluid within tissue. Leg swelling caused by the retention of fluid in leg tissues is known as peripheral edema, or lower limb swelling. Gravity impacts the accumulated fluid and it pools in your legs and feet or arms and hands.
This results from a disruption to the venous circulation system and lymphatic systems or to an interruption of the balance of fluid in your cells.
So…How Does That Happen?
Peripheral Oedema is not a disease, but rather a symptom that indicates your health status, side effects of medications or underlying medical conditions. Before we go through the common risk factors of lower limb swelling, we need to understand how our fluid compartments work.
Fluid is exchanged in the body through intravascular (the vascular system and chambers of the heart) or extravascular (all other interstitial areas) compartments. The fluid balance is maintained by hydrostatic pressures and oncotic pressures. The other two factors that play an important role in fluid balance is vessel wall permeability and lymphatic system.
There can be a number of pathological processes and lifestyle factors that cause an excess of fluid to accumulate within tissue.
Pregnancy
Approximately 80% of pregnant women develop peripheral oedema. This is due to weight gain, hormonal changes and many pregnant women are required to be less active.
The weight gain results in an increase in pressure on the venous system causing lower limb swelling. Pre-eclampsia can also cause peripheral oedema and is a serious condition that requires urgent medical care.
Similarly, Obesity may also lead to peripheral oedema as excess weight causing pressure on veins.
Following Exercise
Exercise, in particular endurance-based exercise, increases the nutrient and oxygen demands on the musculature. As a result, there is an increased demand for blood flow. Metabolites also need to be removed. This increased demand can cause blood to leak out of the vessels into the interstitial tissue spaces and this overpowers the lymph drainage system.
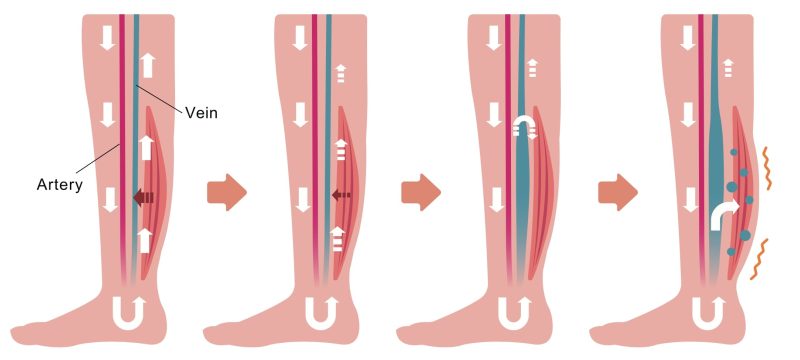
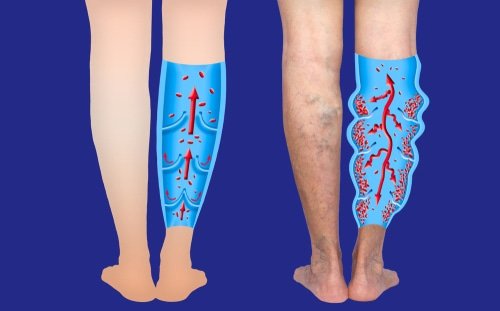
Venous Insufficiency
This is by far the most common cause and develops due to damage to the actual veins or structures inside the veins. Our veins help return blood back to the heart and structures inside the veins, called valves, can become faulty.
These valves prevent the back flow of blood. When they are faulty, the blood pools and begins to leak into the interstitial tissue spaces and this overpowers the lymph drainage system. As a result, the constant pooling of fluid results.
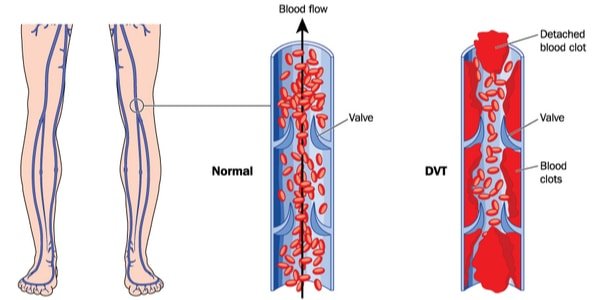
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Leg and foot swelling during air travel is common and typically harmless. The most likely culprit is inactivity during a flight. Sitting with your feet on the floor for a long period causes blood to pool in your leg veins.
But excessive swelling that persists for several hours after you resume activity may be due to a more serious condition, such as a blood clot in the leg, Deep vein thrombosis. If you have swelling in only one leg and also have leg pain, seek immediate medical care!
Drug and Allergy Reactions
Oedema can be a side effect of several common medications. These include blood pressure medications, diabetes medications, anti-depressants, estrogens, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids and vasodilators.
Swelling can also result from allergies to medication, animal bites or food.
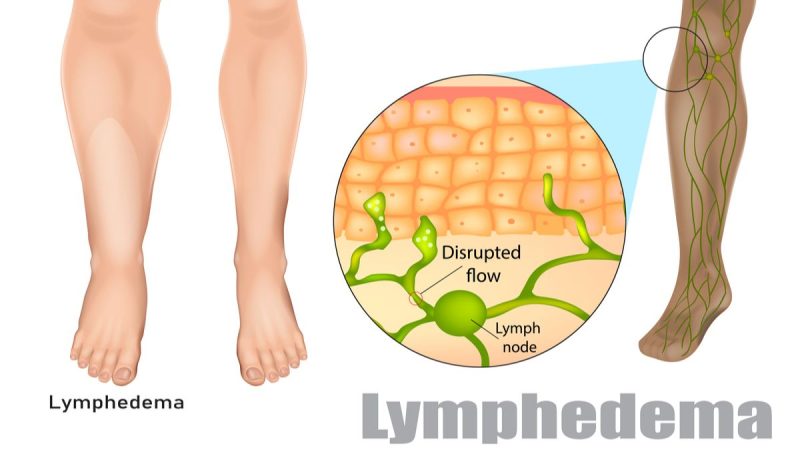
Lymphoedema
This is a condition where fluid retention and tissue swelling are caused by a compromised lymphatic system, which normally helps to remove excess fluid as well as fighting infection. Damage to the lymph system can result from an infection or the removal of lymph nodes secondary to cancer (lymphadenectomy). It can also result from lack of movement or an injury/trauma or inflammation of a limb.
Causes of Disease Processes
Heart failure – if your heart is unable to pump blood to its full capacity, there is a decrease in pressure circulating blood around the body. The extremities are then affected the most as they are further away resulting in even less pressure.
Liver damage – hepatitis or cirrhosis (the liver is damaged by scar tissue) disrupts normal blood flow and disrupts the protein balance leading to peripheral oedema.
Pulmonary hypertension – this results in blood flow not being able to return back to the heart as easily, creating a retrograde pressure on the venous system.
Renal failure/Kidney Failure – as the kidneys lose their ability to function, they create salt and protein imbalances in the blood. This disrupts the normal osmotic homeostasis that exists between cells and also increases the amount of fluid that is retained. As a result, peripheral oedema occurs.
Leg swelling can also be caused by inflammation in leg joints or tissues. You’ll usually feel pain with inflammatory disorders. People suffer from arthritis, gout or bakers cyst behind the knee may also experience lower limb swelling.
Cancer and cancer care management – Pelvic and other cancerous tumors may increase pressure on veins, leading to edema. Peripheral edema may also result from chemotherapy, radiation therapy and other cancer care management.
Malnutrition – a lack of protein can lead to peripheral oedema.
Hormonal changes such as during a menstrual cycle can cause fluid retention.
Care Management
The main focus of your care management should be on managing the underlying cause/s of your peripheral oedema. Simultaneously, of paramount importance, is controlling the fluid that is accumulating in the limbs before it leads to further damage.
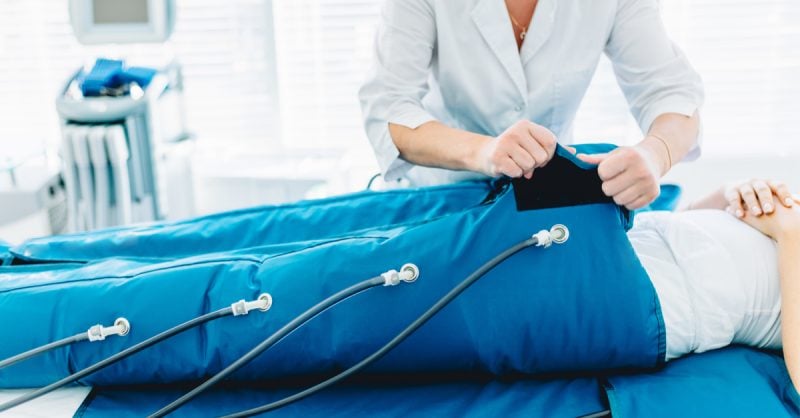
1. Pneumatic Compression
Pneumatic Compression is one of our main care management modalities and is by far one of the most effective.
Pneumatic compression therapy helps to pump the accumulated fluid back through the system of drainage vessels. Its benefits also include
- Accelerates the body’s healing
- Assisting the recovery process
- Eliminating metabolic waste
- Decreases inflammation
- Speeds up the delivery of nutrients for repair to the muscles and soft tissues
2. Exercise
Avoid long periods of standing or sitting. Doing calf raises will help if you are standing or sitting around for a period of time.
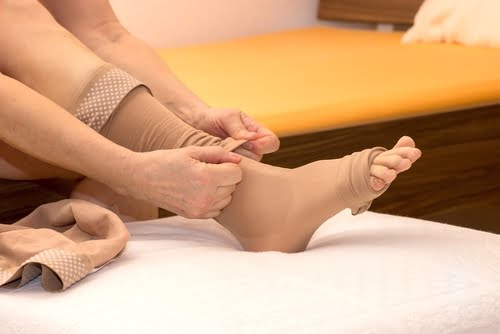
3. Compression Stockings
It helps to delay the accumulation of fluid in the extremities.
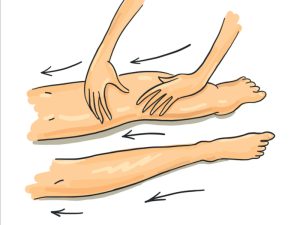
4. Effleurage Type Massage
This can help break up fibrotic tissue and return fluid towards the heart.
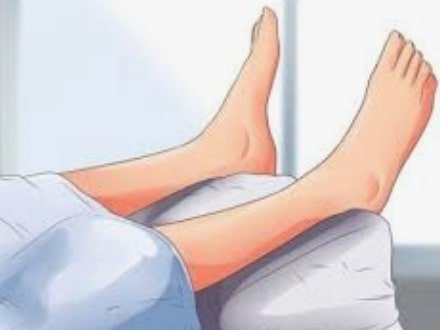
5. Elevation
This elevates the limbs above the level of the heart can help fight gravity and return the blood flow back to the heart.
Consquences of Unmanageed Peripheral Oedema
Peripheral oedema, left unmanageed, can lead to many adverse irreversible outcomes. The chronic swelling causes further damage to the vascular system and surrounding soft tissues. Some of the consequences of leaving peripheral oedema unmanageed include:
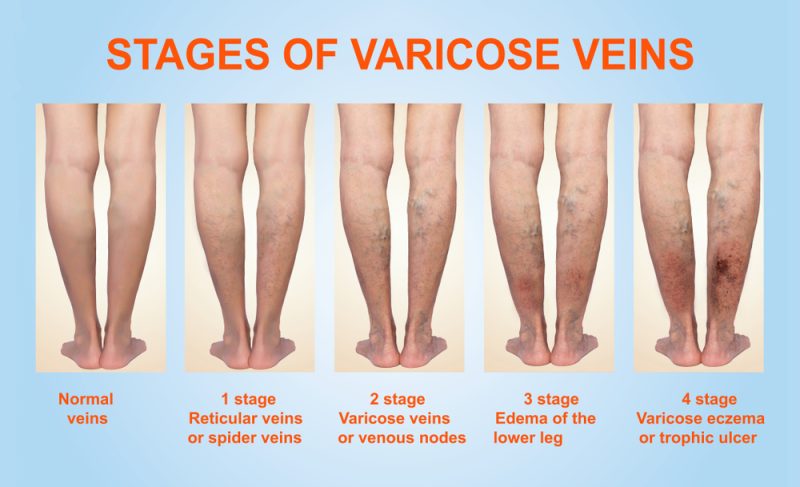
1. More severe varicose veins
In severe cases, a varicose vein may rupture, or develop into varicose ulcers on the skin. These will require care management.
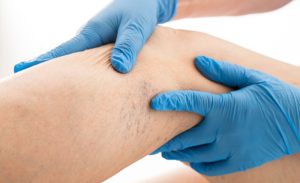
2. Telangiectasia
Also known as “spider veins, this refers to damage to the tiny blood vessels in the lower limbs. These tiny blood vessels balloon and distort and create visible threadlike red lines.
3. Haemosiderosis
This is where the iron in the red blood cells leaks out and stains the skin a brown colour.
4. Pitting Oedema
Due to the extended period of time, the fluid in the lower limbs has been pooling. This chronic stasis of fluid becomes fibrotic. When these fibrotic areas are compressed, they leave a prolonged mark.
Seek Care Management at an Early Stage!
The Podiatry team at My FootDr Singapore is highly trained and skilled at managing and resolving lower limb swelling holistically.