Sesamoiditis
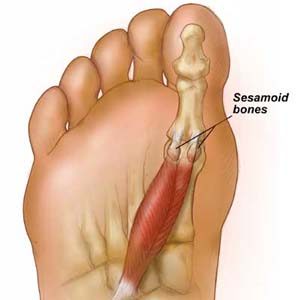
Sesamoiditis is a common ailment of the plantar forefoot, causing pain in the ball of the foot specifically under the big toe joint. The sesamoid bones are very small bones which are located under the big toe joint within the tendons that run to the big toe. They are similar to the kneecap, acting to increase the leverage of the tendons that control the big toe. Due to their location and function, they are subjected to massive pressure and forces every time the big toe is used to push the foot forward.
Symptoms
Sesamoiditis typically presents gradually, starting as a mild ache increasing gradually where it can become an intense throbbing. People participating in activities and sports that involve repetitive, excessive loading of the ball of the foot such as dancing, sprinting or even walking often suffer from this condition. People with boney, higher arched feet, marked flat feet or those who tend to run on the ball of their foot also tend to be more prone to sesamoiditis.
Care Management
Conservative
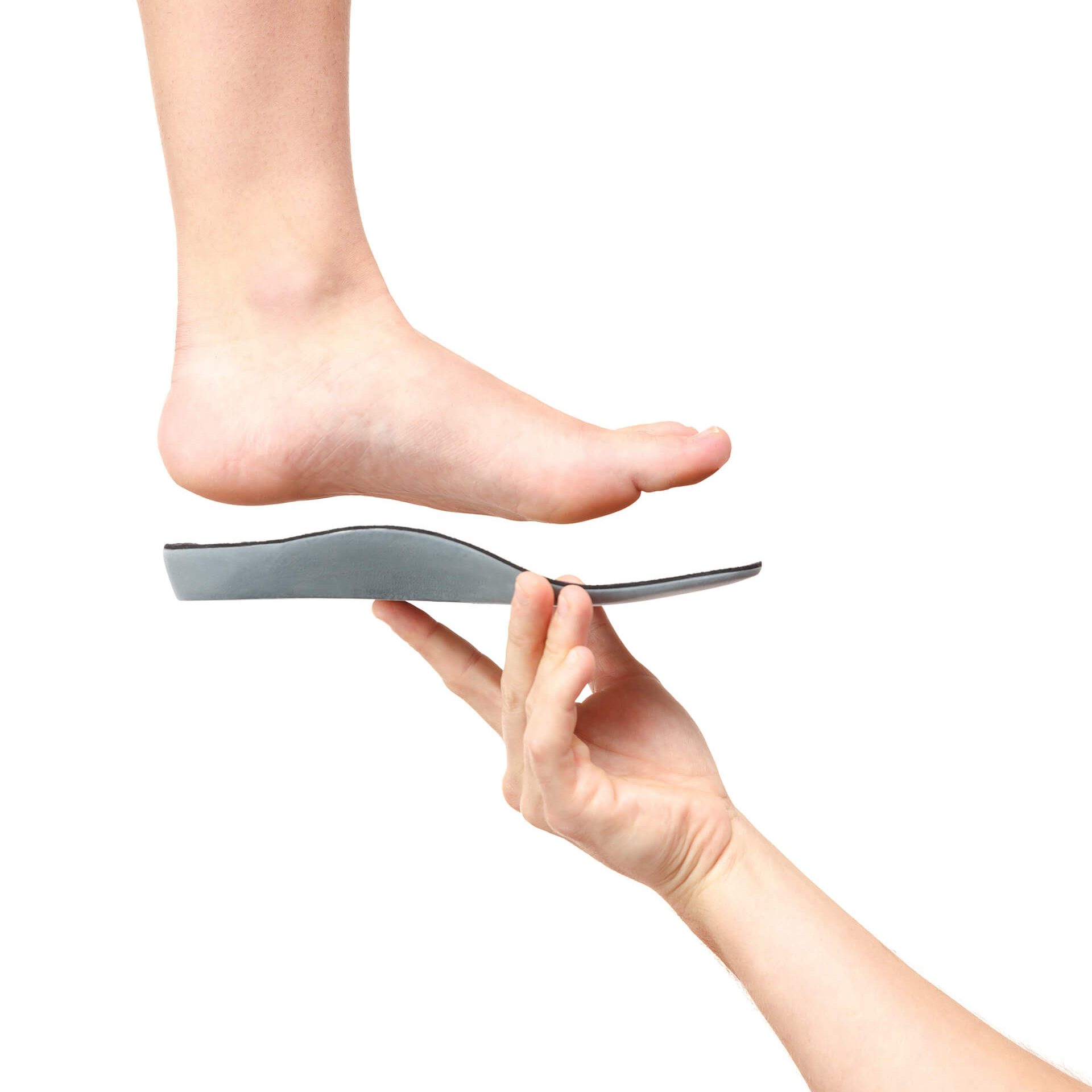
Care Management will vary between patients and will typically involve a period of rest from any activities likely to aggravate the problem. Immobilization strapping, ice and oral anti-inflammatory drugs may also be utilized to settle inflammation and pain and aid in the healing process. A soft full-length functional orthotic is commonly used to offload the sesamoids and deflect pressure away from the painful area. Orthotics are essential in managing an underlying causative foot condition, such as flat feet (pes planus), high arched feet (pes cavus), bunions or those with reduced plantar fatty padding. In the case of persistent severe sesamoiditis or stress fractures of the sesamoids, the use of short leg Pneumatic walker with rocker sole (walking cast) for 2 to 6 weeks may be required. Failing this an injection of steroids or surgery may be considered.
Surgery
In severe cases or following a true fracture of the sesamoids, surgery may be required to remove the damaged or fragmented sesamoid bone. Also in some cases, due to reduced blood supply, there may be delayed or absent healing and a surgical review is warranted.
Expected Outcome
Most individuals will have an immediate improvement in symptoms with conservative care, with total resolution achieved within months. Ongoing management may be recommended in those with an underlying foot condition.